Криптография — важнейший инструмент в защите данных. В C# платформа .NET предоставляет мощные средства для шифрования, подписей и проверки целостности данных.
В данном примере мы создадим цифровую подпись с помощью алгоритма RSA, а затем проверим её — то есть сверим, соответствует ли подпись исходному сообщению.
Что мы реализуем:
Проверку подписи по открытому ключу.
Генерацию ключей RSA;
Подписание сообщения;
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
public class MD5HashHelper
{
public byte[] GetHash(string message)
{
byte[] data;
data = UTF8Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(message);
MD5CryptoServiceProvider md5 = new MD5CryptoServiceProvider();
return md5.ComputeHash(data, 0, data.Length);
}
public bool VerifyHash(string message, byte[] hash)
{
byte[] data;
data = UTF8Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(message);
MD5CryptoServiceProvider md5 = new MD5CryptoServiceProvider();
byte[] hashTemp = md5.ComputeHash(data, 0, data.Length);
for (Int32 counter = 0; counter <= hash.Length - 1; counter += 1)
{
if (hash[counter] != hashTemp[counter])
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
public class DigitalSignatureHelper
{
private RSAParameters m_public;
public byte[] CreateSignature(byte[] hash)
{
RSACryptoServiceProvider RSA = new RSACryptoServiceProvider();
RSAPKCS1SignatureFormatter RSAFormatter = new RSAPKCS1SignatureFormatter(RSA);
RSAFormatter.SetHashAlgorithm("MD5");
m_public = RSA.ExportParameters(false);
return RSAFormatter.CreateSignature(hash);
}
public bool VerifySignature(byte[] hash, byte[] signedhash)
{
RSACryptoServiceProvider RSA = new RSACryptoServiceProvider();
RSAParameters RSAKeyInfo = new RSAParameters();
RSAKeyInfo.Modulus = m_public.Modulus;
RSAKeyInfo.Exponent = m_public.Exponent;
RSA.ImportParameters(RSAKeyInfo);
RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter RSADeformatter = new RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter(RSA);
RSADeformatter.SetHashAlgorithm("MD5");
return RSADeformatter.VerifySignature(hash, signedhash);
}
}
И код формы:
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
namespace DigitalSignature_Example
{
/// <summary>
/// Summary description for Form1.
/// </summary>
public class Form1 : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
internal System.Windows.Forms.Button Button2;
internal System.Windows.Forms.Button Button1;
private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox textBox1;
private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox textBox2;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label label1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label label2;
/// <summary>
/// Required designer variable.
/// </summary>
private System.ComponentModel.Container components = null;
public Form1()
{
//
// Required for Windows Form Designer support
//
InitializeComponent();
//
// TODO: Add any constructor code after InitializeComponent call
//
}
/// <summary>
/// Clean up any resources being used.
/// </summary>
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
#region Windows Form Designer generated code
/// <summary>
/// Required method for Designer support - do not modify
/// the contents of this method with the code editor.
/// </summary>
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.Button2 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.Button1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.textBox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox();
this.textBox2 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox();
this.label1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label();
this.label2 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// Button2
//
this.Button2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(224, 24);
this.Button2.Name = "Button2";
this.Button2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(112, 23);
this.Button2.TabIndex = 5;
this.Button2.Text = "Generate Signature";
this.Button2.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.Button2_Click);
//
// Button1
//
this.Button1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(224, 64);
this.Button1.Name = "Button1";
this.Button1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(112, 23);
this.Button1.TabIndex = 4;
this.Button1.Text = "Verify Signature";
this.Button1.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.Button1_Click);
//
// textBox1
//
this.textBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(120, 24);
this.textBox1.Name = "textBox1";
this.textBox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(96, 20);
this.textBox1.TabIndex = 6;
this.textBox1.Text = "My Signature";
//
// textBox2
//
this.textBox2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(120, 64);
this.textBox2.Name = "textBox2";
this.textBox2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(96, 20);
this.textBox2.TabIndex = 7;
this.textBox2.Text = "My Signature";
//
// label1
//
this.label1.Font = new System.Drawing.Font("Microsoft Sans Serif", 8.25F, System.Drawing.FontStyle.Bold, System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit.Point, ((System.Byte)(178)));
this.label1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(8, 24);
this.label1.Name = "label1";
this.label1.TabIndex = 8;
this.label1.Text = "Set Signature";
//
// label2
//
this.label2.Font = new System.Drawing.Font("Microsoft Sans Serif", 8.25F, System.Drawing.FontStyle.Bold, System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit.Point, ((System.Byte)(178)));
this.label2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(8, 64);
this.label2.Name = "label2";
this.label2.TabIndex = 9;
this.label2.Text = "Verify Signature";
//
// Form1
//
this.AutoScaleBaseSize = new System.Drawing.Size(5, 13);
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(344, 110);
this.Controls.Add(this.label2);
this.Controls.Add(this.label1);
this.Controls.Add(this.textBox2);
this.Controls.Add(this.textBox1);
this.Controls.Add(this.Button2);
this.Controls.Add(this.Button1);
this.MaximizeBox = false;
this.Name = "Form1";
this.StartPosition = System.Windows.Forms.FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
this.Text = "Digital Signature - By Fadi Abdel-qader";
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// The main entry point for the application.
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
DigitalSignatureHelper ds = new DigitalSignatureHelper();
byte[] hash1;
byte[] hash2;
byte[] signedhash;
private void Button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
try
{
MD5HashHelper md5 = new MD5HashHelper();
hash1 = md5.GetHash(textBox1.Text);
signedhash = ds.CreateSignature(hash1);
MessageBox.Show("Подпись создана успешно!");
}
catch(Exception ex){MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);}
}
private void Button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
try
{
MD5HashHelper md5 = new MD5HashHelper();
hash2 = md5.GetHash(textBox2.Text);
if (ds.VerifySignature(hash2, signedhash))
{
MessageBox.Show("Подписи проверены Успешно!");
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Не удалось проверить подписи!");
}
}
catch(Exception ex){MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);}
}
}
}
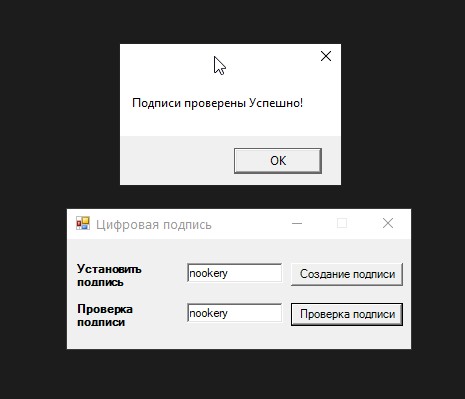
Что здесь происходит:
- Сначала мы генерируем пару ключей RSA (открытый + закрытый).
- Закрытым ключом создается цифровая подпись сообщения.
- Затем проверяем подпись, используя открытый ключ.
- Если данные подменены — проверка не пройдет.
⚠️ Обратите внимание:
- Используется
SHA256— современный и безопасный хеш-алгоритм. RSACryptoServiceProviderможно заменить наRSA.Create()в .NET Core.- Ключи можно сохранять в файлы или использовать в
X509Certificate2.
Вывод
Пример показывает, как легко в C# реализовать базовую защиту данных с помощью цифровой подписи. Это может использоваться в системах обмена сообщениями, лицензировании, документообороте и других сценариях, где важна подлинность и целостность данных.
